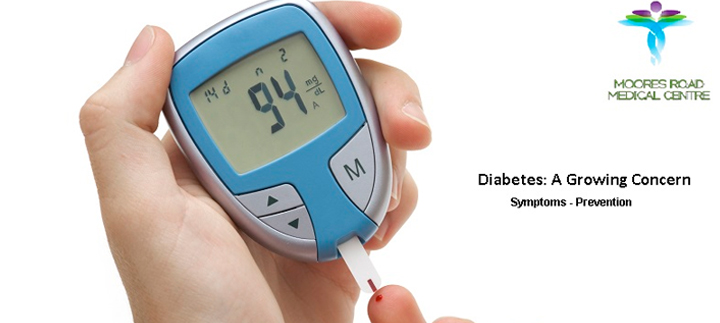
Diabetes is a serious medical condition that affects the way our body handles glucose, a form of sugar, in our blood. It is a growing problem in developing countries. It can lead to dangerous and life threatening health problems. However, if proper precautions are taken, you can stay away from this disease.
Amongst the senior citizens, type 2 diabetes is a growing problem. Apart from seniors, juniors can also be affected by this disease. Type 1 diabetes is generally diagnosed during childhood whereas type 2 is diagnosed in adults and elderly.
Type 2 diabetes generally occurs due to an unhealthy lifestyle. It generally occurs if you:
- are more than 45 years old and are obese or overweight
- are more than 45 years old and have a high blood pressure;
- are over 45 and have a history of diabetes in your family;
- already have had a heart attack before;
- have some heart disease;
- are more than 55 years old;
- have or have had gestational diabetes( diabetes during pregnancy)
- are overweight or obese and also have polycystic ovary syndrome;
- are over 35 years old and an Aboriginal Australian or Torres Strait Islander; or
- are more than 35 years old and are a Pacific Islander, are from a Chinese cultural background or are from the Indian sub-continent
Symptoms
A key issue with elderly people having diabetes is that sometimes they may not develop any symptoms. The general symptoms of diabetes such as feeling thirsty all the time and urinating frequently may sometimes not develop in the elderly. Other symptoms like feeling lethargic and tired are sometimes misinterpreted as part of normal ageing process. As a result, elderly people with diabetes may remain undiagnosed until it leads to some life-threatening diseases. Diabetes is so dangerous that if remains unchecked or undiagnosed, it may damage nearly every major organ like artery damage, kidney damage, eye damage, nerve damage, stroke, heart attack, etc.
Some of the most common symptoms of type 2 diabetes are as follows:
- Excessive hunger
- Excessive thirst
- Blurry vision
- Frequent or increased urination, especially at night
- Sores or cuts that won’t heal
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Skin rashes / itching
Prevention
Preventing the complications of diabetes and minimizing its impacts is vital. To avoid the serious complications of diabetes, it is necessary to do the following things.
- It is important to keep blood pressure, blood glucose and cholesterol under control.
- Changes in lifestyle can help to prevent type 2 diabetes. It is necessary to maintain a healthy weight. Overweight and obese people are at high risk of diabetes. Being obese or overweight can also lead to high blood pressure.
- Having healthy food is very important to avoid the risk of diabetes. Eating a healthy balanced diet also helps to control cholesterol level, blood pressure as well as body weight.
- Staying physically active is also important to prevent type 2 diabetes. Research shows that exercising for atleast 30 minutes 5 days a week can help to reduce the risk of diabetes.
As type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition, a person may need medicine or insulin injections in time if the blood glucose level is not in control. However, by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, this situation can be avoided. It is therefore very necessary to maintain a healthy weight, make healthy food choices and do a regular physical activity. It should not be forgotten that prevention is always better than cure.